
29 September, 2009
Spot the error

07 August, 2009
Win 7 : Win Users 31
The verdict? It's a tale of two operating systems. The one you want, and the one you don't want. The best of upgrades, the worst of upgrades. It's not a far, far better thing than Microsoft has ever done before, but it's not a bleak house either.
Okay, I had a dickens of a good time reviewing it for Computerworld. And 31 feedbacks at computerworld.com seem to indicate that it's a flashpoint for people to throw in their two cents'-worth.
Throw your own barbs into the ring after reading the article. And feel free to be as nasty as possible. I'm thick skinned. I have had to be: I've been working with Microsoft beta code for six months now...
20 July, 2009
CompuServe...site u like?
18 July, 2009
Camera action
Don't try to fight it. Just accept it. And if you need to jump on the bandwagon, do it with a decent quality camera with a decent microphone, not the tinny, blocky, jumpy cellphone footage that comprises most of the embarrassing teen postings.
Here's how to get decent video quality at high definition: scope out these reviews of three HD digital video cameras, which I worked up for a Computerworld article.
These cameras are decent quality, low-budget tools; the quality and content of the footage is up to the cameraman and editor. Or as they say in YouTube, you.
26 May, 2009
Domain steps
http://www.computerworld.com/action/article.do?command=viewArticleBasic&articleId=9132959
I certainly cover more domain hosting issues than domain registration issues, mainly because there's more to write about. You register a domain, it's registered. What you do with it after that...well...there's the rub.
I registered my first domains back in 1996, shortly after Network Solutions started charging some exorbitant amount for what had previously been free. Back then, Network Solutions billed you for $100 for two years' registration. The price later dropped to $70 for a two year period. Then in 1999, more registrars came on board--first Register.com, then a flood of them--and the whole business changed.
The first change was the standard billing period: It became annual instead of biannual. Another result of the competition was that pricing dropped to a "standard discount" rate of fifteen dollars per year per domain, and registrars started to lard on features to attract customers. It's those features that have changed and lowered the barrier of entry to becoming your own d0t-com entity.
The thing that prompted me to pitch this review to Computerworld is that you can now get a domain for around ten bucks a year--with POP email and some kind of site hosting thrown into the bargain.
I'm still amazed by this economy of scale. And if it leads to some confusion between registration and hosting, well, so be it. I'm no McDonald's corporation. I don't need heavy duty hosting. And I don't have a big budget for my online projects either. If I can get satisfaction for the price of a Happy Meal...I'll do it.
12 May, 2009
Space age technology
Oh, how wrong I was before Friday.
I was chatting with one of the scientists who has been working on the Hubble telescope for his entire career, since long before it went up. In the course of a ten minute conversation, I found out a few things that would make earthbound IT pros shudder:
First, the space shuttle mission that blasted off on Monday, May 11th, 2009 was delayed by seven months because of a data router failure. Up in space, a NASA-style Ethernet box went into remission--the kind of thing that IT folk like me could fix a quick trip over to Office Depot and five minutes on site. That pushed back a schedule from October 2008 to mid-May, 2009.
Secondly, the computer systems on Hubble are, to put it mildly, a little behind the times. It went up with a system based around the 386 Intel processor, for one thing. Of course, this was in 1990, when the 386 wasn't quite so prehistoric as it seems to be now. And they did upgrade it later...to a 486, which is what's in there now.
Why the pre-Cambrian technology and glacial repair speeds? It's all about location. To see if they'll survive in orbit, CPUs and routers destined for space need to be tested in harsh conditions--real vacuums, space cold, and cosmic radiation. This takes time. And what takes more time is a tendency to be conservative: The huge distances and cost involved with repair missions in space means that you don't do anything unless you're sure it won't fail quickly. That's why the fastest CPUs in permanent space objects are typically 10 years behind what we earthlings have on our desks.
The third and most significant thing: When anything at all goes wrong on Hubble, it shuts down. At first blush, this sounds pretty inefficient, but it makes sense when you look at the big picture. You've got a massively powerful lens system. You've got a sun nearby with no cloud cover. You've got an expensive space station. And you've got a planet below. Typical childhood experiments with lenses, sunlight, and ants or dried leaves or paper lead to one inevitable conclusion: You don't want that kind of focused energy beaming into the space station--or worse, down to the planet's surface.
That's one kind of cutting-edge technology that you really don't want in orbit around the earth.
07 May, 2009
Mac says "Where's the Active Directory?"
27 April, 2009
Setting up PCs for multiple users
For the past six years, I've been dealing with Windows XP machines that get a lot of use from a lot of people. They sit in school tech labs. They sit in libraries. And they sit in classrooms. Some of them get three hundred people on them in the course of a month. That's three hundred different users logging on multiple times, looking to run different programs and print papers on networked printers. And the way XP works (and it's the same with Windows Vista), that means that there are 300-plus profiles on these computers, tucked away in a folder called Documents and Settings (or in Vista, Users).
If you don't set up the default profile right, you'll spend hours each week dealing with frustrated clients. There are no printers installed. They can't find a program they need, even though you know it's installed. Double sets of icons appear on the desktop. Items in the Startup menu run twice. I know administrators who have struggled with these issues for 18 months or more, and still don't quite have a protocol in place.
Here's the protocol I use for my labs. And trust me...I keep my volume of frustrated clients down to an absolute minimum.
The first step in setting up a new corporate machine is to create a new user. Installer is a good name for him, as an administrator for the local machine and for the domain-based network it will hook up to.
When logged in as Installer, you install all the programs you want each user to have. You set up the icons, desktop pattern, screensaver, Internet Favorites, and Startup menu options that you want every user on the computer to see. And set up all the network printers you want the machine to be able to print to.
As a final step, run all the new programs once to see if they kick up registration or other configuration windows the first time you use them. If you see such a pop-up window, make sure it won't appear next time (because if you don't, every new user on that PC will suffer). When that's out of the way, you've completed the time-consuming but obvious steps. But your job's not over.
While you're still logged in as Installer, open My Computer and disconnect all the network drives (select them, and open Tools, Disconnect Network Drives). Your network log-in scripts will map the drives again, but if you don't remove them, network users without access to these drives will be able to see them but not connect to them. It's tidier and more secure to make sure this doesn't happen.
After disconnecting the network drives, restart your computer using a local administrator account. Go into My Computer, and navigate to C:\Documents and Settings. You should see a few folders there, including Installer, Administrator, All Users, and maybe Default User (this last one's a hidden folder, but you'll see a faint outline of it with the right settings.) These folders contain the files that set up user profiles on this system. If you see any other profiles, delete them.
After this, you need to copy the Installer settings to Default User. To do this, right-click on My Computer, select Properties, click on the Advanced tab, and then the Settings button. Click to select the Installer profile, then click on Copy To. In the Copy To dialog box, click on Browse and navigate to C:\Documents and Settings, then click on Default User and click on OK. If you do it right, you'll see a warning about overwriting a profile. Click OK.
Theoretically, your work should pay off now. But just to be absolutely sure, log on to the computer and the network as a regular user (don't use your regular log-in if you're a network administrator, just to be thorough.) Windows XP should create a new profile for you that's exactly the same as the one you made under Installer, except that your network rights and the drives you can see will be different.
The next just-to-be-sure step is to fire up a program. Anything from Office 2003 or 2007 is good, since it's a particularly finicky program for multiple-user systems. If you're not asked to register or set up the program as a new user, you're golden. If you are, you need to log back on as Installer and rerun the Office installation. Then you must delete the user profile you had the trouble with and try again.
Confused yet? Don't blame the messenger. It's just another day in the life of a system administrator dealing with Windows XP Professional. And we all have days like that, don't we?
Your word processor is no typewriter
So it is with some pleasure that I state that all typing teachers in that era were irredeemably wrong. In fact, they have caused more trouble and expense to computer users than anybody will ever know. As someone who's spent the past 20 years digging up digital documents and correcting them for publication, I can state this with some authority. Without exception, well-trained typewriter typists make messy digital documents. Oh, their documents may print out all right, but their redundant spaces and tabs make any attempt to edit or change a font an exercise in frustration.
These are the top four typewritten crimes against word processing:
Crime 1: Entering two spaces after a period. Typewriters couldn't adjust letter spacing, so typing teachers taught students to hit the spacebar twice so it was easy to see the end of a sentence. Word processors handle spacing automatically, so there is no good reason to do this anymore. In fact, it looks terrible.
Crime 2: Hitting the Tab key to indent a line. This terrible habit was the only way to do it with a typewriter. It's a waste of effort now that you can pre-format your document. If you have a document with a hanging indent (where each line except the first one is indented), it's a labor-intensive nightmare, especially when you need to make corrections.
Crime 3: Using combinations of tabs and spaces to line up text. Ever heard of word processed tables? You will. Read on.
Crime 4: Hitting the Enter key twice to space out paragraphs. Once again, a waste of effort. One that I occasionally commit, but really shouldn't.
So how do you do it right?
When you open your document, set the page layout right away. In Microsoft Word, press Ctrl+A to select the entire document, then pick Format, Paragraph. In the Indentation section, under Special, select First Line. Under Spacing, select the Auto option under Before. If you need to double-space, select that here too.
When you want to make two or more columns, don't use tabs. Instead, create a table with the right number of columns. In Word, select Table and Insert, and make the columns right. Then when the table appears, drag to highlight the whole thing, and select Borders and Shading. Click on None to ensure you won't see the lines on the table when you print it out.
How to Clean Up a Mistyped Document
Of course, if you correct a document that's already messed up, it will look even more of a mess. So you need to know a few clean-up tricks using the search and replace tool. In Microsoft Word, you open the dialog box with Ctrl+H or the Edit, Replace menu. Tidying up the two-spaces-after-a-period crime is easy: In the Find What box, enter a period and two spaces. In the Replace With, enter a period with one space. Presto!
Tabs and paragraph returns are harder to replace automatically, because you can't hit a Tab or Enter key in a search-and-replace box. But you can enter the code for these characters: ^t and ^p. Hold down the Shift key and press 6, and you've got that caret symbol (^). Follow it with a P for paragraph return or T for a tab.
Undoing the tabbed indent crime becomes easy, then. In Find What, enter ^p^t. In Replace With, enter ^p and click the Replace All button. Undoing the double-return crime is also easy: replace ^p^p with ^p and click Replace All.
Now, inspect your document. You may find a few indents made up of spaces. These can be removed by replacing ^p followed by a space with plain ^p and hitting Replace All several times, until Word tells you there were no changes made.
About the only residual problem I've ever found after going through these steps are blocks of data that used to look like tables and weird page breaks because people hit Enter five or more times to get over the page.
Page breaks are best handled in Word by holding down the Ctrl key and pressing Enter. This inserts a page break symbol.
Copying blocks of data out of "tables" made up of tabs is requires a little-known Alt key trick: Hold down the Alt key and use the mouse to draw a selection box around a column of text. Once you've selected what you need, cut it and paste it into a real Word table.
Now you've unlearned all the bad habits you learned from typing teachers, make sure the next generation doesn't commit them: Buy your kids a $30 copy of Type To Learn 3 from Sunburst Software (www.sunburst.com). In fact, if you still hunt-and-peck, buy it for yourself and try it out for a while. It's better for your wrists than online gaming, and it's kind of fun too. Best of all, it's guaranteed not to shout at you for typing poetry when you're done with your exercises.
06 April, 2009
Easter Eggs we have loved: The Hall of Tortured Souls
 The Hall is a 3-D walkthrough environment, where the arrow keys control movement. These instructions will get you into the hall:
The Hall is a 3-D walkthrough environment, where the arrow keys control movement. These instructions will get you into the hall:
1. Open Excel 95 with a blank worksheet
2. Go down to row 95 (that Windows 95 branding strikes again)
3. Select the whole row
4. Tab over to column B
5. Go to Help/About
6. Hold down Ctrl + Alt +Shift and click on the Tech Support Button.
7. The Hall of Tortured Souls window appears.
Once you're there, The C and D keys tilt the point of view down and up. You can walk through walls, but you need to be careful, as walls without windows can trap you inside the wall when you plough into them.
There are three levels, each with four rooms, and three pools you can walk across. On the bottom level, you appear to reach a solid wall, but behind it is a a zig-zag path. You get to the path by typing a cheat code, excelkfa, a nod to the Doom all-power cheat code IDKFA.
But there are no demons to blast into oblivion, so to many gamers, it lacks punch. When you're done exploring, X out of the box and quit Excel. You can always go back another day.
Easter Eggs we have loved: Word 2
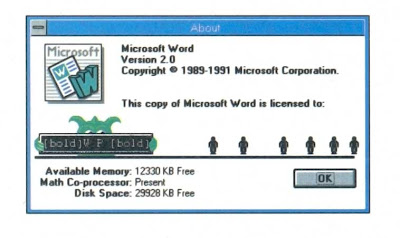 I don't know what you were doing in 1991, but Word for Windows 2.0 was crushing its competition--literally. Hidden away in Microsoft Word's About box were six crudely animated stick figures who jumped up and down on a green monster carrying the banner WP. That was obviously short for WordPerfect, and judging from the victory dance and firework display after the WP Monster had been bounced below the baseline, the little guys were the WinWord programmers.
I don't know what you were doing in 1991, but Word for Windows 2.0 was crushing its competition--literally. Hidden away in Microsoft Word's About box were six crudely animated stick figures who jumped up and down on a green monster carrying the banner WP. That was obviously short for WordPerfect, and judging from the victory dance and firework display after the WP Monster had been bounced below the baseline, the little guys were the WinWord programmers.2. From the Tools menu, select Macro, then Record Macro.
3. Enter the macro name SPIFF, and either press Enter or click the Edit button.
4. In the Macro box, delete the lines Sub Main and End Sub and the blank lines between.
5. Close the menu and save the changes.
8. Open the Help menu, then click About Microsoft Word.
9. Click once on the Word logo icon in the upper-left corner.
Easter Eggs we have loved: Excel 4
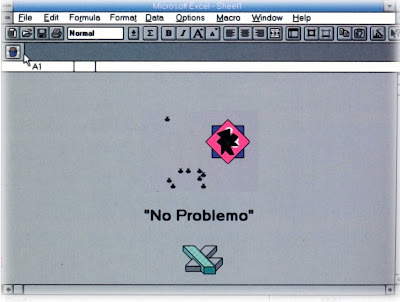 At the top of the Easter egg list for sheer mean-spiritedness, we have Excel 4.0. Microsoft's coders weren't content with being poised to corner the market on Windows-based spreadsheets back in 1992. They wanted to hold the leading DOS-based spreadsheet--Lotus 1-2-3--up to public pillory.
At the top of the Easter egg list for sheer mean-spiritedness, we have Excel 4.0. Microsoft's coders weren't content with being poised to corner the market on Windows-based spreadsheets back in 1992. They wanted to hold the leading DOS-based spreadsheet--Lotus 1-2-3--up to public pillory.Holy Week! It's Easter Egg Time!
Well, thank goodness Mozilla still operates like a real software company. Their Firefox 3.0.3 has some lovely bits of vintage hacker humor stuck away, and they're easy to release.
In a new browser window, enter the address about:mozilla and press Enter. You'll be treated to pseudo-biblical verse touching obliquely on money-grubbing companies that make other browsers, and how the old Mozilla browser became Firefox:
Mammon slept. And the beast reborn spread over the earth and its numbers grew legion. And they proclaimed the times and sacrificed crops unto thefire, with the cunning of foxes. And they built a new world in their own image as promised by the sacred words, and spoke of the beast with their children. Mammon awoke, and lo! it was naught but a follower.
from The Book of Mozilla, 11:9(10th Edition)
A more recent and funnier Egg touches on a few science fiction nerves. In the Address bar, type in about:robots and press Enter.

03 April, 2009
.Mobi isn't half of a Melville classic
Call me Ishmael. Go ahead, I dare you. Call me Ishmael, because frankly I'm at sea when it comes to understanding what the sponsors of the dot-mobi domain space were thinking. The mere dot-com, dot-net, and dot-org suffixes were not enough for them. They needed something that sounded epic, a whale of a good idea, and so they came up with their own top-level domain: .mobi. But beneath the surface lurks, well, not very much, really.
Now, almost three years after the sun rose on the .mobi domain, my opinion holds fast.
If you've missed the dot-mobi story so far, here's a quick summary: Back in May 2006, the sponsors of a mobile top-level domain (mTLD) began sunrise preregistration of domain names with the delightful-sounding dot-mobi suffix. The sponsors included all the big mobile players: Ericsson, Google, Microsoft, Nokia, Samsung Electronics, T-Mobile, and Vodafone. The idea was to create a forum just for mobile users, serving up pages specially designed for mobile platforms.
A noble idea, for sure, but most people believe that a top-level domain (TLD) is not really the proper forum for this.
If you've missed the TLD story so far, the dot-com, dot-net, and dot-org domains were designed in the early 1990s to create separate spaces for separate entities--specifically commercial enterprises, networks, and nonprofit organizations. Other top-level domains appeared in the years that followed: dot-info and dot-museum, for example, for all-information sites and museums.
The waters became muddy almost immediately. Individuals and companies rushed in and registered domains at will, either not knowing or not caring what the TLDs really mean. To domain registrants, a d0t-com was a way to brand themselves on the Internet, and if a dot-com wasn't available, a dot-net or dot-org would suffice. And when it came to later waves of d0t-whatevers, a museum is both an information source and a nonprofit, so surely dot-info and dot-org apply to them just as much as dot-museum does. The result? Most museums just use dot-org domains.
Of all the best-known top-level domains, only dot-edu and dot-gov seem to have remained pure.
By 2004, the point of the top level domain space was so lost to the world at large--including ICANN, the body that's supposed to regulate it--that two really bad ideas appeared: .mobi and .xxx. At the time, the creator of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee strongly condemned them both. The notion of a .xxx red light district was utterly impractical to enforce, and little more than a springboard for political posturing. But Berners-Lee reserved his real disapproval for the .mobi idea: It actually undermined one of the fundamental points of the Internet: It's supposed to be device-independent, so restricting a top-level domain to a single class of devices is just plain wrong. And if the Founder of the Web disapproves of something that much, people should at least think about it.
But that didn't happen. After all, philosophy has not been the driving force behind Web development. It became market driven almost immediately, and remains that way. So what are Web content providers to think? Should they register dot-mobi domains to protect their trademarks? Or should they concentrate on making mobile-friendly sites and promote their wares or services or ideas in some other way?
That’s up to them, of course, but I have my own opinion.
The real way to attract mobile users to mobile Web services is to design your Web site well for a handheld device. Having spent months at a time launching and relaunching Web sites over the past fifteen years, I can hear the collective groan from Web creative teams. But as every tourist board knows, if you want the visitors, you have to make the destination appealing.
As things stood in 2006, the Net came in a limited form to mobile users. But many Web developers put in the effort to attract people by creating really mobile-friendly sites. Reuters mobile, Google News mobile, BusinessWeek, and the BBC looked fantastic on a BlackBerry.
Google news also did a good job because it stripped down the news pages from outside sites into a mobile-friendly format. Mobile Web search also had strong showings from the XHTML version of Google, the Answers.com mobile, and the WAP version of Yahoo.
With the real work of integrating more advanced Web services, such as Web mail, IM, contact address books, calendars, and photos, Yahoo did yeoman’s work with its Yahoo Go for Mobile portal services, albeit in mid-2006 reaching only Symbian OS phones in the Nokia 60 series and available only via Cingular.
What lurks beneath
In the past three years, none of the sites that worked at creating the first mobile-friendly content profited much from the dot-mobi domain. And the ones that did smelled a bit too fishy for my taste.
Take the domain auction site Sedo for example. They took their cut on the auction that sold Flowers.mobi for $200,000 in 2006. A year later, they took an even bigger cut from the sale of Music.mobi ($616,000), Games.mobi ($401,500), Sports.mobi ($101,000), Movies.mobi ($82,000), and Videos.mobi and Photos.mobi ($51,000 apiece).
Who’d sink that much money into a mess of domain name, and why? The who is Alvaro Albarracin. The why, according to his 2007 blog entry: "I am not planning on developing these names, I am planning on selling these sometime in the near future."
So the .mobi domain space has become the equivalent of the tulip bulb in 16th century Holland: a commodity with no intrinsic value except as a token in the game of Speculation.
In short, the .mobi domain space amounts to another gambling forum. And as every gambler knows, the house always wins. The house in this case is the people who administer the domain space:
- The registrars take your fifteen bucks in registration money
- ICANN that takes a cut of that
- and the real money, and it is really big money, goes to the group that created the dot-mobi domain space
That last group comes off looking pretty unethical. Even if you assume there's nothing wrong with marketing-fueled free market speculation, it's ony ethical if you play fair. But they really didn't. Not content to create a spurious domain space and take administration fees for running it, they reserved the really lucrative names for themselves. They didn't allow speculators to register high-profile names like sports.mobi; they put a hold on generic names they deemed attractive and staged auctions to sell them off to the highest bidder.
Here's an example of the kind of press release they sent out to announce their scheme:
DUBLIN, Ireland and WASHINGTON, D.C.– September 23, 2008 – dotMobi – the company behind the .mobi internet domain designed to help consumers find mobile-friendly content – today announced a special online auction for 200 highly desired premium .mobi domain names including actors.mobi, bands.mobi, blackjack.mobi, boys.mobi, cellphones.mobi, doctors.mobi, games.mobi, homeloans.mobi, house.mobi, model.mobi, quotes.mobi, racing.mobi, stamps.mobi, vip.mobi and xxx.mobi.
As part of its ongoing series of unique methods of allocating Internet domain names, dotMobi is working with Sedo, the market leader in online domain name auctions, to launch the auction on November 5, 2008.
Doesn't anyone know what conflict of interest means anymore? This release would be a damning piece of evidence, if anyone cared enough about ethics to prosecute a case against these profiteers. It's not as evil as the kind of Ponzi scheme that sank Wall Street, but something about the whole .mobi scene smells like bilge water to me.
Or perhaps I'm being a bit too jaded. For all I know, the may be some good in the dot-mobi space. There may be dot-mobi sites with real value for those who are communicating or disseminating information or entertainment to the masses. Do you have any favorite .mobi sites? Do you think I’m being the other half of Herman Melville’s magnum opus? If so, you know what to do. Call me "Ishmael". Go ahead. I dare you.
01 April, 2009
Slashdotted!
My retrospective on operating systems we have known and loved and said goodbye to--a Computerworld.com feature called Gone But Not Forgotten--got picked up at the den of tech ennui, Slashdot, and commented into oblivion. It was a marvelous experience that reminded me of being a Sysop on a Ziff-Davis forum on CompuServe in the early 1990s. I've always enjoyed the posturing of the techier-than-thou crowd, and it's good to see that it's still in full force.
In fact, responses to the article broke down in the standard distribution pattern from the old forum days:
29 March, 2009
Domain transfers: 1and1 to GoDaddy
I’ve already written a column about the information you need to collect before transferring a domain from one registrar to another. Here are the steps I went through to transfer two domains I had at 1and1.com to GoDaddy.
Day 1
The first step is to go to the registrar you want for the next year. You pump in your domain names and they’ll tell you the domains are already registered. There’s usually a link that reads “I’m the owner of these domains and I want to transfer them.” If not, there’ll be another link that reads “Transfers” where you can put in one or more domain names you want to transfer.
In this round of transfers, GoDaddy offered transfers at $6.99 with a one-year renewal on the domain, so I signed up to transfer two domains, a .info and a .com, currently registered at 1and1.com. The order confirmation comes through in a confirmation note almost immediately. I’d clicked like lighting to get the transfer registered, and repented at leisure. Two domains at $6.99 equals $13.98, right? Wrong.
QTY ITEM PRICE
--------------------------------------------------------------
1 .INFO Domain Name Transfer - 1 Year $7.19
1 .COM Domain Name Transfer - 1 Year $7.19
$7.19 each? Not $6.99? Darn GoDaddy. I forgot they slap on an “ICANN fee” surcharge of 20 cents. They make it sound like a tax. It’s not a tax. It’s GoDaddy being mealy-mouthed about passing on their cost of doing business to their customers. A few other registrars do the same, and it always ticks me off because it’s basically a dishonest way of making your prices look lower than your competition’s. But GoDaddy’s a bit of a cowboy operation that way. From their blustering CEO downwards, GoDaddy seems like an operation that’ll do whatever it takes to get customers—in good or bad taste, honest or deceptive--as long as they stay basically legal. But they offer a pretty good price and set of features, so I’ll stick with them for now.
DOMAIN NAME TRANSFER - Initial Authorization for Registrar Transfer
Re: Transfer of .COM and .INFO
Dear Oneandone Private Registration,
GoDaddy.com, Inc. received a request on 3/3/2009 for us to become the new registrar of record.
You have received this message because you are listed as the Registered Name Holder or Administrative contact for this domain name in the WHOIS database. If you are not the Account Holder, or you are transferring the domain to a new owner, please forward this email to the appropriate Account Holder so that they may complete the transfer process.
1and1 apparently forwards to their anonymous account holders. Excellent…and less work for me. (Why did I choose GoDaddy over 1and1, I began to wonder).
The next step is for me to follow a link in this email to a transfer acknowledgement page run by GoDaddy. It contains a request for an AUTH code, which 1and1.com keeps secrete on the domain administration page for the domains I’m transferring. I log in there, get the code, pump it into the transfer acknowledgement page and my work is done. All I need to do now is wait…and wait…and wait…
Day 6
I get another Transfer Acknowledgement email from GoDaddy. Didn’t I do this already? Well … apparently not for my .INFO domain.
So “to complete your recently requested transfer, we must receive approval of the administrative contact currently associated with the domain name(s) below”, so I do that.
And wait…and wait…and wait…
DAY 12
Oh, frabjous day! I get my confirmation telling me that my domains are officially now at GoDaddy. Twelve days for a transfer’s about right. I always give it at least four weeks in case there’s some kind of problem. And there almost always is. Yet somehow, here is how the e-mail started:
=====================================================
DOMAIN NAME TRANSFER CONFIRMATION
=====================================================
Congratulations! The transfer request for the following domain name(s) has been completed
Could I possibly have got through a domain transfer with no problems? I’ve had lots of them in the past. I’ll blast past some crucial step and find out a week later that the whole process has failed. Then I’ll have to go back at get a credit at the new registrar, and then start the process all over again. It’s a nuisance I’m anxious to avoid.
I read the confirmation e-mail over one more time, just to set my mind at rest. It didn’t. Naturally, I’d forgotten one crucial final step, which GoDaddy reminded me about:
IMPORTANT!
IF THIS DOMAIN IS NOT CURRENTLY HOSTED, follow the instructions below to change your domain name servers to our parked servers. By doing so, you will avoid possible charges from your prior registrar and enable your domain's new features now that your transfer is complete.
Agh! When you transfer a domain from one registrar to another, it transfers the complete record…including the Nameservers that host the domain. I’d had the domain hosted at 1and1 for ten months and not really done much with it. The $60 a year in hosting fees had seemed pretty reasonable, but I’d not actually developed the site at all, so it actually amounted to flushing sixty bucks a year down the toilet. And with the six-month billing cycle coming up, I had cancel the hosting fast.
So I did. And by doing so, I averted a billing disaster.
The whole process, including two days it took to cancel hosting and get a pro-rated rebate on the hosting I’d already paid for was two weeks. My domains were now safely over at GoDaddy, where I turned on domain forwarding so that anyone tapping in the address would be brought straight to an existing web page on another server.
One of the domains comes straight here. Another goes to another blog I run. And it’s using free blog services like these that saves me sixty bucks a year (and countless hours of mucking around in HTML) in developing a Web site to go with each of my domains. So maybe I do have more sense than domains. But on the other hand, I do have quite a few domains.
25 March, 2009
Happy birthday, dear Unix
With your birth as our starting point, then, let's look at the biggest desktop OS milestones of the past 40 years.
1969
Unix was brought to life on a spare DEC PDP-7 at AT&T Bell Labs. When AT&T decided to abandon the Multics (Multiplexed Information and Computing Service) operating system on its minicomputers, Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie cobbled together an operating system so they could continue to play a space travel game that Thompson had developed. A colleague gave the system a jokey name based on Multics -- UNICS, the Uniplexed Information and Computing Service, which morphed into UNIX or Unix.
1976
Intergalactic Digital Research's maverick brain Gary Kildall creates CP/M, a simple microcomputer operating system for simple microcomputers. It would be the model for command-line DOS variations for two decades.
1977
The godfather of open source is born when the Computer Systems Research Group at UC Berkeley releases a variant on Unix called the Berkeley Software Distribution. BSD will ultimately spawn alternatives to some commercial microcomputer operating systems -- and form the core of at least one major commercial operating system, Mac OS X.
Tandy/Radio Shack introduces a line of affordable home computers, and debuts a family-friendly operating system called TRS-DOS with such Rated-M-for-Mature commands as KILL. Other companies' versions of DOS substitute the less menacing DEL command, for Delete.
For the rest of this story, head on over to Computerworld.com!
18 March, 2009
Outlook could not install the custom actions
Outlook could not install the custom actions. The object could not be found
This tenacious little error message popped up for our long-suffering admin staff every time they tried to open a message or create a new one. As you can imagine, it got irritating very quickly.
It's because of a corrupt Forms cache, which needs to be deleted. The fix runs like this:
1. Close Outlook.
2. Under C:\Documents and Settings find the folder for the user who's experiencing the problem.
3. Make sure under the Tools, Folder Options menu that system files are not hidden.
4. Navigate to \Local Settings\Application Data\Microsoft\FORMS, and delete the file FRMCACHE.DAT.
Then clear out and restart Outlook. You'll get a quick flashing dialog telling you that the form is being regenerated, and everything should be fine.
16 March, 2009
Domain transfers: Step 1
You've got...a domain name.
Don't worry. One of the best-kept secrets of the domain world is that you're not stuck with the registrar you picked last year. You can transfer any domain you've got successfully from one registrar to another...as long as you get all your ducks in a row beforehand.
Before you start a transfer, log in at your current domain registrar, navigate to the domain management pages, and pay attention! Make sure you get through all the details in this checklist. If you've already started a transfer, don't panic. Just get cracking on these details quickly. You've got a few days to get it all straight.
(a) Check the start date. Make sure you’ve had the domain for at least 60 days. ICANN won’t let you transfer a domain that’s been at a registrar for any less.
(b) Check the expiration date. Make sure there’s at least two weeks left on the registration—preferably a lot more. Any less, and the domain may expire before the transfer is complete.
(c) Check the contact information. Make sure that you are listed as the domain’s Admin contact, and that the contact information is current.
(d) Check your e-mail. Make sure that you’re able to receive e-mails from your old registrar—you’ll be doing a lot of e-mail monitoring in the next few days. To ensure that your old registrar isn't being spam-filtered, make a minor change to your domain record—add your middle initial to your name, or change the format of your phone number. The domain registrar will automatically inform you of any change—if you get an e-mail from them, you know you’re okay.
(e) Get your Auth Code. An Auth Code is a special password required for transferring .com, .net, .info, .org, .biz, .name and .us domain names. Look for the term Auth Code anywhere in the domain administration site. Each registrar handles these codes differently. Some put them right there in the domain record (1and1,com, for example). Others, including GoDaddy, make you click on a link and send Auth Codes by e-mail. DirectNIC used to make you open a trouble ticket in its private support message area and give it to you there. Whatever your registrar demands, do it before you start the transfer process, and keep the Auth Code on hand. You’ll need it later.
(f) Cancel any extra services at your old registrar. If you got your domain as a package deal with a hosting package, you may end up getting billed for hosting services you no longer use. When transferring domains away from 1and1,com, for example, you need to visit cancel.1and1.com, sign in using your account number and password, and fill out a cancellation form. Then you need to respond to an auto-generated e-mail and log in again—or 1and1.com will continue to think you’re still a subscriber.
(g) Unlock your domain! Most registrars lock your domain by default. It's a sensible precaution against unscrupulous domain-nappers, but it does mean that not even the legit owner of the domain can do anything with it. Make sure the domain is unlocked and click on Save. You'll get an e-mail about this, and it may make you confirm your choice. Once you have...you're done with Phase One of the process.
Now keep all your details handy, and get ready to monitor your e-mail carefully. You’re ready for step two: Starting the transfer.
[to be continued]
12 March, 2009
On the Download: Biennesoft's YouTube Downloader 2.1.7
Or if you're a teacher trying to string together some source material for a lesson or extract a classic speech from someone's hokey slideshow--what can you do?
I'll tell you what: You can download Biennesoft's YouTube Downloader 2.1.7. It's a simple program with two main functions: First, it downloads the Flash video files from YouTube and Yahoo Video and Daily Motion and a host of other video hosting sites. Then it converts that video into something you can play on your PC, Mac, iPod, cellphone, or PlayStation Pro.
YouTube Downloader looks deceptively basic, but it has hidden depth. A lot of thought went into making it easy to use--and Biennesoft doesn't even charge you money for all that work. You fire it up, go to YouTube or another video site, copy the URL of the video you like to the Clipboard, and when you switch over to YouTube Downloader--there's the URL, snatched straight out of the Clipboard.
Click the download button, and it gets the video onto your hard drive. Here's the good bit though; once the video is on your computer, you click the button again, and it converts the video from the FLV format into something you can use: iPhone, iPod, PSP, AVI, WMV, and Xvid. Or it can extract the soundtrack from a video and make an MP3 out of it. There's even a basic video editor that lets you crop out bits you don't like.
I've known people to jump through many hoops to perform the tasks that YouTube Downloader handles in two clicks. I've been one of those people. Thankfully, now I can devote all the time I used to spend in getting videos onto an offline player actually enjoying them.
List price: Free
Where to get it: http://download.cnet.com/YouTube-Downloader/3000-2071_4-10647340.html

11 March, 2009
On the Download: Defrag, De Whole Frag, and Nothing but Defrag
 Hold onto your propeller hats, team, I'm about to rhapsodize over a defragmentation program.
Hold onto your propeller hats, team, I'm about to rhapsodize over a defragmentation program.No! Wait! Don't click away from the page! I know that recommending a defragger is like recommending a dental floss. It's not exciting. It's not even interesting. It's tool for a chore, for goodness sake. But stick with me, here. I'm serious about this. If Smart Defragger 1.11 were a dental floss, it would keep your teeth shiny and your breath sweet and it wouldn't leave stringy bits between your molars. It's really that good.
So why bother talking about hard disk chores like defragging at all? Well, it's amazing how fast Windows and its applications frag up your hard disk. And you'd be surprised much faster a computer can run when you optimize a badly fragmented disk. And it's not only about speed: In the lab I was managing six years ago, heavily fragmented disks caused programs to crash and lose work for dozens of frustrated students. Defragging cured the problem right away.
That's why I have a two-step plan when anyone complains about how slow or flaky their system is running. First, fire up MSCONFIG and weed out all the dross that loads when you start up Windows. (Yes, Adobe Reader tray icon, Microsoft Office loader, and Real scheduler...I'm talking about you.)
Then defrag the disk.
The trouble is that Microsoft's Windows Defrag program is like the Victory brand goods in George Orwell's novel 1984: The only show in town, and pretty darn awful. The trouble is that nobody wants to pay extra to get decent third-party defragmenter, no matter how elegant and efficient it is.
So let's see whether I can persuade anyone to try out Smart Defrag 1.11. Put away your wallets. It's a free download, with no strings attached. If you want to toss a donation at IOware in gratitude, they'll take it. And they deserve it.
Smart Defrag is really darn good. It takes up almost no RAM, so it's good for old creaky systems as well as spanky new ones. It analyzes and defrags at a zippy pace on any Windows platform from 98 up. It can be scheduled to perform routine defragmentation at specific times of the day (say, lunchtime). And it can performa a deep optimize that organizes your hard disk's contents so that the most frequently used files are at the front of the line, ready to load fast.
It's also ridiculously simple to set up: Run it once. Set an automatic defrag time. Forget about it.
That's all, folks. Simple, free, and without fuss. And it won't let your system slow down over time or crash for no apparent reason. So do yourself a favor and get it.
And don't forget to floss.
04 March, 2009
Don't Buy My Domain! An Epilogue
It’s an odd thing, but you never forget a domain that you once owned. I have registered dozens over the past few years. Some I developed. Some I registered for other people, and helped them to develop. And others, I let slip through my fingers.
As a case in point, a decade ago I was called upon to register a domain for a how-to article for PC World. At the domain registrar (Register.com, if I remember correctly), I typed the first thing that came to mind--my own name--and found the domain was available. I registered it, but I never intended to waste good money and time actually developing it. It expired a year later, and it's had one careful owner ever since. (I assume he has the same name as me.) I still check back on that site from time to time to see how it suits him. Frankly, it fits him better than it ever fit me.
So over the 16 months that have passed since an entrepreneur in Pune, India, bought a domain from me at auction, I have checked back periodically to see what's going on. I have an intellectual curiosity, of course, but I also have a mild tinge of paranoia—I originally registered that domain along with one other for a side business of mine, and I’m wondering if I sold a plum domain name to a rival who’ll take away my business.
As it turns out, I needn’t have worried. Every time I have visited the site, the same sight met my eyes: an Under Construction sign. I’m not a great businessman myself (I flogged my only cyber-asset for the price of a dinner and a night in a three-star airport hotel), but I somehow expected my buyer to have grand plans. I almost hoped for a worthy rival who would spur me on to great heights in my side-business. But it was not to be. In fact, last week when I pumped the URL into my browser Address bar, nothing happened. There was no Under Construction site. There was nothing.
I nipped over to my favorite state-of-the-domain site, BetterWHOIS.com, where anyone can check up on the status of any domain. There it was in black and white: The domain I sold 16 months ago had expired on January 19th. It was in a status called RedemptionPeriod.
The end of life for a domain is a complicated procedure. Like all things to do with the domain name space, it’s regulated by ICANN—the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers. After a domain name expires, the registrar (in this case, GoDaddy) has 45 days to notify the owner that their domain name is going to be dropped from the registry. This seldom happens by accident—most registrars default to an automatic renewal setting. But if the domain name is dropped, ICANN guidelines call for a 30-day grace period during which the owner can reclaim it. After this grace period, there’s another holding period, after which the name is dropped from the registry and anyone can claim it.
I’ve had dealings with GoDaddy for years, and they can sometimes be a bit slow about things. It took them more than a month to pass the payment over to me, for example. So I have no idea how long it’ll take them to release the expired domain. Conventional wisdom says the term is 30 days plus a 5 day holding period, but they’re already more than two weeks past that. Another piece of conventional wisdom is that the registrars don’t let anyone know when they’re releasing domains because there are sharks circling in the pool that expired domains drop into.
The domain drop pool is full of drop-catchers—professional domain speculators looking for saleable domains. You could hire one to snap up an about-to-drop domain if you were desperate to get it. In fact, GoDaddy will gladly charge you $80 for the service. I considered hiring them on for about three seconds. But that service is too pricey and too speculative for my tastes. Besides, it has a faint whiff of conflict of interest to me.
So I’m going to wait for the domain drop to happen and take my chances. But just to be on the safe side, I will continue NOT to tell you the name of the domain I’ve been blogging about all this time. I don’t want to fight with any of you over this thing. We’ve got too much history together.
Buy My Domain, Episode 3
The time: Last year
The scene: My e-mail inbox.
Dear Matt Lake,
You have received an offer for Item Number 1XX2O27 in the amount of $250.00. Log in to your account to view the offer.
It took me a couple of seconds to understand what this email was all about. I nearly trash-canned it. Then I cast my mind back 14 months and remembered: I’d put an old domain up for sale. And now, someone was trying to buy it from me. Well, there was a turn-up for the books.
I scrambled to look through my notes and noticed that the bid was considerably lower than GoDaddy’s estimate ($622 or higher). But it was higher than Afternic’s estimate of $200. And it was more than three times more than the $79.95 I’d sunk into the project.
So on one hand, I wasn’t an online entrepreneur of the order of Filo and Yang, Jeff Bezos, or Steve Case. But on the other hand, I’d made out better than if I’d stuck the cash in a money-market, or just spent it on outsized latte drinks at Clusterbucks. So I decided to take the money.
I had 72 hours to respond, so I hied myself over to GoDaddy’s Domain Name Aftermarket and started in on the process. Little did I know, it would take a month of waiting around and responding to various emails, and frankly, it was a bit irritating.
Day 1
I accepted the bid. Within the hour, I got the delightful message “Congratulations! The domain name Item Number 1XX2O27 has sold! Please do not accept any transfer requests of this domain at this time!”
I am told to wait and let GoDaddy handle the transaction. They’ll act as an escrow agent to ensure everything goes smoothly. This sounds good to me, so I wait.
Day 3
GoDaddy is pleased to inform me that they have received the proceeds for the sale of my domain. I am to log on and contact the buyer to begin the domain transfer process.
To do this, I must first unlock the domain to allow the domain transfer to proceed. Then I must collect the buyer’s account information to enter into a form somewhere on the site. This I do.
Day 5
GoDaddy sends email to tell me that I have initiated a change of registrant for my domain. I already knew this--I was there after all--but at least they're acknowledging the fact. Two days late, true, but they're acknowledging it.
Day 12
GoDaddy sends me another email with slightly different phrasing to tell me that I have initiated a change of registrant on my domain. If I meant to do this, I don’t need to do anything more. Yep, I did it alright. Nine days ago.
Day 18
GoDaddy tells me that the change of registrant went through. A second email dated one second after the first one tells me I have cancelled my account for the domain. I do a double-take on this one, and then realize that it’s a good thing. So I wait for the next dispatch--and my money.
Day 19
GoDaddy sends me a courtesy note to tell me that the whole transaction will be completed on a date ten days in the future.
Day 24
GoDaddy sends me the exact same courtesy note to tell me that the whole transaction will be completed on a date five days in the future.
Day 29
GoDaddy tells me that the transaction is completed. That’s great.
Now…where’s the money?
Day 34
GoDaddy PayPals me the money.
So there we have it. Nearly sixteen months after I started this process, a polite entrepreneur in Pune, India, paid me $250 for my domain. It wasn’t a coup like the sale of business.com to RH Donnelly in 2007 (that netted more than $300 million), but it was good enough for me.
The question was: Was it good enough for my buyer? What did he want to do with the domain now that he acquired it?
This all happened more than a year ago, so I’ve been tracking the domain ever since. So I know exactly what he did with it. And I’ll share that information with you. A little more promptly than GoDaddy shared the revenue for the sale all those moons ago.
[TO BE CONTINUED]
My balance sheet:
Expenditures: $29 in registration fees; $39.95 in appraisal fees; $10 in membership fees; $12.50 in Godaddy sales commission; various state, federal, and business taxes.
Total expenditures: $91.45 total plus tax
Total revenues: $250
Net gain: $118 minus tax
Total hours expended…who knows? But I’m sure that divided up, I earned roughly minimum wage out of the deal.
Buy My Domain, Episode 2
The time: A couple of years ago
The scene: GoDaddy's domain resale site, The Domain Name Aftermarket (now auctions.godaddy.com).
I figured I'd try to add to its curb appeal a little to see if I could get close to the appraised price. Step one: Put up a nice little welcoming Web page. Instead of displaying generic "for sale" or "parked" signs, I put up a sample live page demonstrating what the domain could be used for--and, of course, slapped a little "for sale" link leading to the domain auction.
Brilliant though this ploy was, it failed to elicit a single bid at auction. But it did improve the look of the lot, so it seemed like a good thing to do. And so did goosing up the listing a little, though this wasn't as easy. The Domain Name Aftermarket allowed 255 characters to describe an auction lot. Even to someone trained in the noble art of making text fit into highly designed magazine pages, that's quite a restriction.
Then I had a brainstorm: Why not get more hard evidence of my domain’s value? Why not get a second evaluation? At the time, TDNAM was a new kid on the block. Afternic was the grand master of domain name resale—they’d been around for a decade longer than Godaddy’s site. So I threw good money after bad and paid $20 at Afternic for a second appraisal. And it hurt. Afternic reckoned that the current market value of my domain was $200. Ouch! That was less than a third of what GoDaddy had estimated. Afternic reckoned that the domain's potential market value was $1,100—with significant development, of course—and that was about $600 less than the top end of TDNAM's evaluation.
But I’m an honest seller and wanted to look like one, so I cited Afternic's appraisal URL in my auction listing. I thought this made me look like a man with nothing to hide, one who showed due diligence, and one who wasn’t out for a quick buck. Exactly the kind of person I'd like to buy from.
Because it cost me as much as a hardback book, I actually read the advice Afternic sent along with its appraisal. It was generic but it reinforced what I’d already worked out for myself:
· Include the fact that you've had your name appraised. It lets potential buyers know that a third party has assisted in estimating the value.
· Feel free to use all or part of your appraisal notes.
· Always have your domain names pointed somewhere. When someone types in your domain name, have it point to your auction page, your domains-for-sale site, or even a one-page site with your contact information.
Check on the first and third items. I even made a nod to the second item in the one-page site I’d put up. So I'd now followed the best advice of the old lags in the market, and I upped the curb appeal on my little corner of the domain real estate market. I'd done just about everything I could to raise its profile short of taking out an ad in Computerworld.
And all this work increased the number of bids at the auction from zero to zero.
So I shelved the project, but kept my options open. I kept my membership in GoDaddy’s aftermarket site, renewed my domain for another year, and left the domain for sale at Godaddy.
Someday, I reasoned, someone would want to buy that domain.
I was right. But that day wasn’t coming anytime soon.
[TO BE CONTINUED]
My price tag so far:
$29 in registration fees; $39.95 in appraisal fees; $10 in membership fees
$79.95 total
Buy My Domain, Episode 1
To begin at the beginning: I registered a domain for $15 at Directnic.com, transferred it the following year to Godaddy.com for $7, and sat on it for six months. Then I asked myself the question: Where can you sell domain names? A couple of years ago when this story began, the obvious choices were Afternic and Godaddy’s Domain Name Aftermarket (which is now called GoDaddy Auctions). They're still the obvious choices.
A quick look at these venerable domain aftermarket sites taught me two things:
1. People do buy second hand domains
2. People who sell them ask ridiculous prices for them, and seldom get them.
Something about TDNAM.com appealed to me: It had buyers. They were actually paying a couple of hundred bucks apiece for such names such as coffeefair.com, endsuffering.com, and my personal favorite, kungfujesus.com. My domain wasn’t quite as catchy, but it was short and businesslike and well-suited to a real moneymaking market. So I thought it stood a chance of making a modest profit.
To make sure I didn’t price myself out of the market, I needed to set a fair price, and that was the problem: What's a fair pirce? Luckily, most domain name aftermarket venues charge a small fee to analyze a domain name and figure out what the market will bear for such a name. I paid five bucks to get an automated appraisal from TDNAM.com, which shared some good news: This site (a GoDaddy property, remember) reckoned from a superficial analysis that the domain could fetch somewhere between $722.00 and $2,094 on the open market.
But how realistic is that figure? TDNAM.com didn't really explain their calculations--and the range was huge--so those figures could have been plucked out of thin air. However, TDNAM did offer a higher-end "seal of approval" appraisal for $14.95. This certified appraisal gives you the right to flag any domain you sell in their marketplace so that prospective buyers can see the appraised value.
The news wasn't as good this time around. The appraised value of my precious cargo was now $622 to $1,617--a C-note off the low end and almost a grand off the high end.
But at least it gave me a access to their appraisal methods--and these are valuable to anyone who wants to speculate in the domain name market. In a nutshell, these are the important factors:
Short domain names sell well; names with numbers, letters, and hyphens do not.
Words that are in vogue help jack up the price of a domain; generic names less so.
A dot-com domain will sell better than any other extension, such as .net, .org, or .biz.
And that's about it. The rest is in the details.
So there I was with a domain in my portfolio appraised between $622 and $1,617, ready to bring it to market. The question: When the gavel dropped, would it fetch anything near the appraised value?
[TO BE CONTINUED]
My price tag so far:
$22 in registration fees; $19.95 in appraisal fees
$41.95 total
Sites mentioned in this article:
Afternic.com
03 March, 2009
I want my MPC--but I'm not going to get it
For many years, I had no qualms about recommending Gateway very highly for its support. Their computers were fine and fairly priced, nothing too special, but nothing bad either. But all other things being equal, I used to recommend Gateway to more or less all my clients without reservation because Gateway support was so stellar.
This started to go south in the fall of 2007, when Gateway divested its corporate support division to an ID-based company called MPC Computers. Opening a trouble-ticket or getting driver downloads, which had been as simple as entering a serial number at gateway.com, turned into a multilayered morass of spawned browser windows. The support transition seemed to go badly for everyone. Dealing with MPC was as frustrating for its own front-line support staff as it was for the callers.
Shortly afterwards, underlying trouble began to surface. In May 2008, MPC received a notice from the American Stock Exchange stating that they were "not in compliance with Section 1003(a) (i) of the AMEX Company Guide, in that the company's stockholder equity had fallen below $2 million dollars." By late October 2008, MPC ceased to be traded publicly. By November 7, 2008, the company declared bankruptcy.
Meanwhile, many of my sources have griped about getting minimal or nonexistent help for in-warranty Gateway woes. It's been frustrating on one level and sad on another to see how far the mighty have fallen.
If there's an upside to this--and it's a very minor one--it's that MPC Computer will be liquidating its assets in a 3-day public auction in Nampa, ID, starting next Wednesay at 10am. The auction will also be webcast, so if you want to snap up bargains or just watch the aftermath of a train wreck , check out www.mpccorp.com for details.
02 March, 2009
Batch Conversions R Us
Many complaints circle around the .docx format from Office 2007 not working in Office 2003, but that's surprisingly easy to handle. The real pain is distributing MOVs to Windows users who don't want to install Quicktime, or handling batches of antiquated data in abstruse file formats. (Ami Pro docs anyone? Works database files?)
I have two relatively cheap programs in my quiver that have proved invaluable.
For hard data files, Dataviz's Conversions Plus has been a staple of my software toolkit for more than a decade. It can translate all manner of obscure file formats into something you'll recognize, and power through gigabytes of old files in minutes. It's plain, it's simple, and it works. End of story. Except that it's about fifty bucks to license the download.
For video files, I have been using AVS Video Converter for about a month. MOVs, AVIs, MPEGs, WMVs...it handles them all. Of course, re-encoding video takes an age, and you need to know your output settings to prevent something you want on DVD coming out formatted for an iPhone, but AVS seems to have the task in hand. It's about sixty bucks to license the download.
My only gripe is that Dataviz's program doesn't yet have Office 2007 formats in its quiver. I hold out hopes...
Office compatible? Kinda
I stand by that, but last weekend, I found all three of these applications deficient in one word processing task I do all the time in Microsoft Word.
That task is search-and-replace on paragraph returns. I've had to repurpose so many documents that have paragraph returns at the end of each line that I can twitch the solution in Microsoft Word.
It's a three-step process: Replace the two paragraph returns with a string of characters that you know won't exist anywhere in the document (I use four @ signs). Remove all the other paragraph returns and replace them with a space. Then reinstate the true paragraph returns.
For good measure, you then remove all instances of two spaces, just in case you inadvertantly introduced them. Unless there's any hyphenation in the original document, you should end up with a perfectly formatted document at the end.
Of course, you need to know one more trick: Microsoft Word's secret code for a hard paragraph return. It's ^p (shift-6 gives you the circonflex symbol, followed by a lowercase p).
It's a great trick to use in Word. But as of 28 Feb 2009, it didn't work in Google Docs, Open Office, or Zoho.
Okay, Sun, Google, and Zoho, I know this is an incredible obscure feature, but couldja add it, huh? Huh? Huh? It'll make at least one user happy.
It's not a reason to upgrade, but...

The antidote for dumb mistakes
...and you can, kind of. In practically every situation you find yourself in Windows and Windows software, and in most Mac apps too, remember: Control Z.
Hold down the Ctrl key. Press the Z key. Presto!
The last thing you did is undone.